Distributed Caching: Core Fundamentals
11 January, 2020 - 3 min read
Distributed Caching
Distributed caching is a critical technique for enhancing the performance and scalability of applications, especially in the era of microservices and cloud-native architectures. The article focuses on understanding its principles, advantages, and implementation strategies to design efficient and robust systems.
What is Distributed Caching?
Distributed caching involves storing cache data across multiple servers or nodes instead of a single server. This approach helps in distributing the load, improving fault tolerance, and ensuring high availability of cached data.
Key Benefits
- Scalability: By distributing cache data across multiple nodes, you can scale horizontally. Adding more nodes can handle increased load without degrading performance.
- High Availability: Data is replicated across nodes, ensuring that the cache remains available even if some nodes fail.
- Reduced Latency: Cached data is closer to the application servers, reducing access time and improving response times.
- Load Balancing: Distributed caching helps in balancing the load across different nodes, preventing any single node from becoming a bottleneck.
How Distributed Caching Works
Architecture
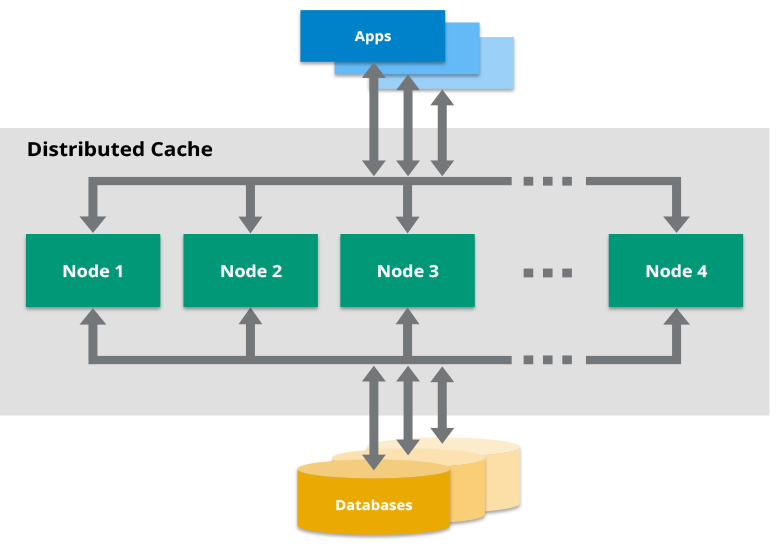
A typical distributed caching architecture consists of:
- Cache Clients: Application servers that interact with the distributed cache.
- Cache Servers: Nodes that store the cached data.
- Coordination Mechanism: Ensures consistency and synchronization across cache nodes.
Data Distribution Strategies
- Hashing: Consistent hashing is commonly used to distribute data across nodes. It ensures even distribution and minimizes data movement when nodes are added or removed.
- Sharding: Data is divided into shards, and each shard is assigned to a different node. This approach simplifies the distribution but requires effective shard management.
Consistency Models
- Strong Consistency: Ensures that all nodes have the latest data, which is critical for applications requiring up-to-date information.
- Eventual Consistency: Guarantees that data will eventually be consistent across nodes, suitable for applications where immediate consistency is not crucial.
Implementation Strategies
Popular Tools
- Redis Cluster: Provides a distributed and scalable in-memory key-value store with automatic sharding and replication.
- Memcached: A distributed memory caching system designed for simplicity and speed.
- Hazelcast: An in-memory data grid that offers distributed caching, computing, and messaging capabilities.
Best Practices
- Cache Invalidation: Implement effective cache invalidation strategies to ensure data consistency.
- Monitoring and Metrics: Continuously monitor cache performance and utilization to identify bottlenecks and optimize accordingly.
- Data Expiry Policies: Define appropriate expiry policies to prevent stale data and manage memory efficiently.
Conclusion
Distributed caching is an essential technique for building high-performance, scalable, and resilient applications. By distributing cache data across multiple nodes, developers can achieve better load distribution, reduced latency, and higher availability. Understanding the principles and best practices of distributed caching is crucial for mid to senior level developers to optimize their application performance and ensure seamless user experiences.
This article provided a high-level overview of distributed caching, targeting mid to senior level developers. For more in-depth information, consider exploring the documentation and best practices of the mentioned tools.